vnstat sur Raspberry Pi pour surveiller le trafic réseau
By Pierre-Alain B on Saturday, June 4 2016, 14:58 - Permalink
Nous allons voir ici comment installer vnstat pour surveiller le trafic réseau et afficher une petite page de synthèse sur l'utilisation du trafic. Cela peut-être utile par exemple pour mesurer le trafic traversant une passerelle Raspberry Pi construite tel que raconté ici.
vnstat en ligne de commande
Tout commence avec (e.g. sous Raspbian Jessie) :
apt install vnstat vnstati
Demandons alors à vnstat de créer une base de données du trafic pour l'interface que l'on veut surveiller :
vnstat -i eth0 -u
Désormais, un appel à la commande vnstat affiche en ligne de commande une synthèse sur le trafic réseau :
vnstat -u #Mise à jour des informations
vnstat #Affichage de la synthèse
Database updated: Sat Jun 4 13:02:00 2016
eth0 since 29/05/16
rx: 136.26 MiB tx: 411.92 MiB total: 548.18 MiB
monthly
rx | tx | total | avg. rate
------------------------+-------------+-------------+---------------
May '16 134.72 MiB | 410.23 MiB | 544.94 MiB | 1.67 kbit/s
Jun '16 1.55 MiB | 1.69 MiB | 3.24 MiB | 0.09 kbit/s
------------------------+-------------+-------------+---------------
estimated 8 MiB | 8 MiB | 16 MiB |
daily
rx | tx | total | avg. rate
------------------------+-------------+-------------+---------------
29/05/16 134.72 MiB | 410.23 MiB | 544.94 MiB | 51.67 kbit/s
today 1.55 MiB | 1.69 MiB | 3.24 MiB | 0.57 kbit/s
------------------------+-------------+-------------+---------------
estimated 1 MiB | 1 MiB | 2 MiB |
vnstat sur une page web
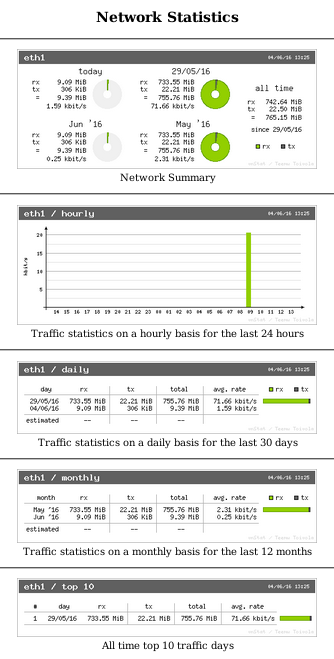
vnstati est une commande parente de vnstat qui génère une image de synthèse plutôt qu'un tableau. Pratique pour nous, êtres humains, qui aimons la bigarrure ! Alors demandons à vnstati de nous géréner quelques images à l'aide de ce script que l'on pourra placer dans cron :
#!/bin/bash vnstat -u -i eth0 vnstati -s -i eth0 -o /var/www/html/summary.png vnstati -h -i eth0 -o /var/www/html/hourly.png vnstati -d -i eth0 -o /var/www/html/daily.png vnstati -t -i eth0 -o /var/www/html/top10.png vnstati -m -i eth0 -o /var/www/html/monthly.png
Et pour afficher ces images, nous allons utiliser une petite page web et nginx :
apt install nginx
puis remplaçons la page par défaut /var/www/html/index.nginx-debian.html par index.html contenant :
<!doctype html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>Statistics</title> </head> <body> <h2 align="center">Network Statistics</h2> <hr align="center"> <p align="center"><img src="summary.png" alt="Summary"/><br/> Summary </p> <hr align="center"> <p align="center"><img src="hourly.png" alt="Traffic stats on a hourly basis for the last 24 hours "/><br/> Traffic stats on a hourly basis for the last 24 hours </p> <hr align="center"> <p align="center"><img src="daily.png" alt="Traffic stats on a daily basis for the last 30 days"/><br/> Traffic stats on a daily basis for the last 30 days </p> <hr align="center"> <p align="center"><img src="monthly.png" alt="Traffic stats on a monthly basis for the last 12 months"/><br/> Traffic stats on a monthly basis for the last 12 months </p> <hr align="center"> <p align="center"></p> <p align="center"><img src="top10.png" alt="All time top 10 traffic days"/><br/> All time top 10 traffic days</p> <hr align="center"> </body> </html>
et si l'on pointe un navigateur vers l'adresse IP du Raspberry Pi, on voit alors s'afficher :